Co Element
Periodic Table
0
Symbol
Co 0
Group Number
9 9
Period Number
4 4
Block
d block 0
Element Family
Transition Metal 0
CAS Number
7440484 38
Space Group Name
P63/mmc 0
Space Group Number
194.00 5
Facts
0
Interesting Facts
- The main source of Cobalt is as a by-product of copper and nickel metal mining.
- Cobalt metal can be obtained from other elements like Oxygen, Sulfur and Arsenic.
- It s also used in electroplating process as it exhibits anti cession properties.
Sources
Found in Compounds, Mining, Ores of Minerals 0
History
0
Who Discovered
Georg Brandt 0
Discovery
In 1732 0
Abundance
0
Abundance In Universe
3 * 10-4 % 9
Abundance In Sun
~0.0004 % 9
Abundance In Meteorites
0.06 % 10
Abundance In Earth's Crust
0.00 % 21
Abundance In Oceans
0.00 % 20
Abundance In Humans
0.00 % 17
Uses
0
Uses & Benefits
- Its alloys with aluminum and nickel are used to make powerful magnets.
- Few other alloys exhibit high-temperature strength and hence they are used in Turbines of Jet and Gas engine.
Industrial Uses
Chemical Industry, Electrical Industry, Electronic Industry 0
Medical Uses
Pharmaceutical Industry 0
Other Uses
Alloys 0
Biological Properties
0
Toxicity
Toxic 0
Present in Human Body
Yes 0
In Blood
0.04 Blood/mg dm-3 18
In Bone
0.04 p.p.m. 27
Physical
0
Melting Point
1,495.00 °C 29
Boiling Point
2,870.00 °C 34
Appearance
0
Physical State
Solid 0
Color
Gray 0
Luster
Metallic 0
Hardness
0
Mohs Hardness
5.00 8
Brinell Hardness
470.00 MPa 26
Vickers Hardness
1,043.00 MPa 11
Speed of Sound
4,720.00 m/s 14
Optical Properties
0
Refractive Index
Not Available 0
Reflectivity
67.00 % 11
Allotropes
Yes 0
α Allotropes
α-Cobalt 0
β Allotropes
β-Cobalt 0
γ Allotropes
Not Available 0
Chemical
0
Chemical Formula
Co 0
Isotopes
0
Known Isotopes
26 13
Electronegativity
0
Pauling Electronegativity
1.88 12
Sanderson Electronegativity
2.56 1
Allred Rochow Electronegativity
1.70 5
Mulliken-Jaffe Electronegativity
Not Available 0
Allen Electronegativity
1.84 10
Electropositivity
0
Pauling Electropositivity
2.12 41
Ionization Energies
0
1st Energy Level
760.40 kJ/mol 19
2nd Energy Level
1,648.00 kJ/mol 31
3rd Energy Level
3,232.00 kJ/mol 22
4th Energy Level
4,950.00 kJ/mol 19
5th Energy Level
7,670.00 kJ/mol 12
6th Energy Level
9,840.00 kJ/mol 12
7th Energy level
12,440.00 kJ/mol 11
8th Energy Level
15,230.00 kJ/mol 12
9th Energy Level
17,959.00 kJ/mol 13
10th Energy Level
26,570.00 kJ/mol 7
11th Energy Level
29,400.00 kJ/mol 8
12th Energy Level
32,400.00 kJ/mol 8
13th Energy Level
36,600.00 kJ/mol 8
14th Energy Level
39,700.00 kJ/mol 9
15th Energy Level
42,800.00 kJ/mol 12
16th Energy Level
49,396.00 kJ/mol 11
17th Energy Level
52,737.00 kJ/mol 13
18th Energy Level
134,810.00 kJ/mol 1
19th Energy Level
145,170.00 kJ/mol 2
20th Energy Level
154,700.00 kJ/mol 4
21st Energy Level
167,400.00 kJ/mol 4
22nd Energy Level
178,100.00 kJ/mol 3
23rd Energy Level
189,300.00 kJ/mol 3
24th Energy Level
Not Available 100
25th Energy Level
Not Available 100
26th Energy Level
Not Available 100
27th Energy Level
Not Available 100
28th Energy Level
Not Available 0
29th Energy Level
Not Available 0
30th Energy Level
Not Available 0
Electrochemical Equivalent
1.10 g/amp-hr 57
Electron Work Function
5.00 eV 5
Other Chemical Properties
Chemical Stability, Ionization 0
Atomic
0
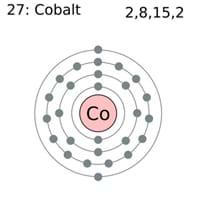
Atomic Number
22 84
Electron Configuration
[Ar] 3d2 4s2 0
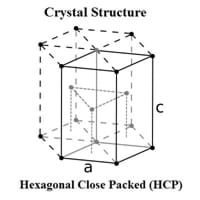
Crystal Structure
Hexagonal Close Packed (HCP) 0
Crystal Lattice
HCP-Crystal-Structure-of-Cobalt.jpg#100 0
Atom
0
Number of Protons
22 83
Number of Neutrons
26 62
Number of Electrons
22 83
Radius of an Atom
0
Atomic Radius
147.00 pm 34
Covalent Radius
160.00 pm 30
Van der Waals Radius
200.00 pm 28
Atomic Weight
47.87 amu 78
Atomic Volume
10.64 cm3/mol 46
Adjacent Atomic Numbers
0
Previous Element
7 0
Next Element
22 0
Valence Electron Potential
95.20 (-eV) 10
Lattice Constant
295.08 pm 61
Lattice Angles
π/2, π/2, 2 π/3 0
Lattice C/A Ratio
Not Available 0
Mechanical
0
Density
0
Density At Room Temperature
4.51 g/cm3 70
Density When Liquid (at m.p.)
4.11 g/cm3 49
Tensile Strength
434.00 MPa 9
Viscosity
Not Available 0
Vapor Pressure
0
Vapor Pressure at 1000 K
Not Available 0
Vapor Pressure at 2000 K
0.98 (Pa) 14
Elasticity properties
0
Shear Modulus
44.00 GPa 17
Bulk Modulus
110.00 GPa 15
Young's Modulus
116.00 GPa 18
Poisson Ratio
0.32 12
Other Mechanical Properties
Ductile 0
Magnetic
0
Magnetic Characteristics
0
Specific Gravity
4,500.00 1
Magnetic Ordering
Paramagnetic 0
Permeability
Not Available 0
Susceptibility
Not Available 0
Electrical Properties
0
Electrical Property
Poor Conductor 0
Resistivity
420.00 nΩ·m 12
Electrical Conductivity
0.02 106/cm Ω 42
Electron Affinity
7.60 kJ/mol 37
Thermal
0
Specific Heat
0.52 J/(kg K) 9
Molar Heat Capacity
25.06 J/mol·K 44
Thermal Conductivity
21.90 W/m·K 43
Critical Temperature
Not Available 0
Thermal Expansion
8.60 µm/(m·K) 45
Enthalpy
0
Enthalpy of Vaporization
429.00 kJ/mol 15
Enthalpy of Fusion
15.48 kJ/mol 19
Enthalpy of Atomization
468.60 kJ/mol 15
Standard Molar Entropy
27.30 J/mol.K 56
|
||
|
||
|