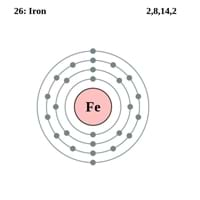
Fe Element
Periodic Table
0
Symbol
Fe 0
Group Number
8 10
Period Number
4 4
Block
d block 0
Element Family
Transition Metal 0
CAS Number
7439896 88
Space Group Name
Im_ 3m 0
Space Group Number
229.00 1
Facts
0
Interesting Facts
- Iron is not always magnetic in nature, its allotrope are ferromagnetic and the B allotrope is nonmagnetic.
- The blood consists Iron in hemoglobin molecules to transfer Oxygen in the body.
Sources
Earth's crust, Found in Minerals 0
History
0
Who Discovered
Unknown 0
Discovery
Before 5000 BC 0
Abundance
0
Abundance In Universe
1.1 * 10-1 % 1
Abundance In Sun
~0.1 % 1
Abundance In Meteorites
22.00 % 1
Abundance In Earth's Crust
6.30 % 2
Abundance In Oceans
0.00 % 12
Abundance In Humans
0.01 % 5
Uses
0
Uses & Benefits
- Iron metal alloy steel is used in the application of civil engineering and manufacturing.
- Alloys of iron with nickel, vanadium, chromium, tungsten and manganese have very useful properties.
Industrial Uses
Aerospace Industry, Automobile Industry, Chemical Industry, Electrical Industry, Electronic Industry 0
Medical Uses
Pharmaceutical Industry, Surgical Instruments Manufacturing 0
Other Uses
Alloys, Sculptures, Statues 0
Biological Properties
0
Toxicity
Non Toxic 0
Present in Human Body
Yes 0
In Blood
447.00 Blood/mg dm-3 3
In Bone
380.00 p.p.m. 5
Physical
0
Melting Point
1,535.00 °C 25
Boiling Point
2,750.00 °C 37
Appearance
0
Physical State
Solid 0
Color
Gray 0
Luster
Metallic 0
Hardness
0
Mohs Hardness
4.00 10
Brinell Hardness
200.00 MPa 40
Vickers Hardness
608.00 MPa 18
Speed of Sound
5,120.00 m/s 8
Optical Properties
0
Refractive Index
Not Available 0
Reflectivity
65.00 % 12
Allotropes
Yes 0
α Allotropes
Ferrite (alpha Iron) 0
β Allotropes
beta Iron 0
γ Allotropes
gamma Iron 0
Chemical
0
Chemical Formula
Fe 0
Isotopes
0
Known Isotopes
26 13
Electronegativity
0
Pauling Electronegativity
1.83 14
Sanderson Electronegativity
2.20 7
Allred Rochow Electronegativity
1.64 8
Mulliken-Jaffe Electronegativity
Not Available 0
Allen Electronegativity
1.80 12
Electropositivity
0
Pauling Electropositivity
2.17 40
Ionization Energies
0
1st Energy Level
762.50 kJ/mol 17
2nd Energy Level
1,561.90 kJ/mol 36
3rd Energy Level
2,957.00 kJ/mol 29
4th Energy Level
5,290.00 kJ/mol 16
5th Energy Level
7,240.00 kJ/mol 16
6th Energy Level
9,560.00 kJ/mol 14
7th Energy level
12,060.00 kJ/mol 15
8th Energy Level
14,580.00 kJ/mol 14
9th Energy Level
22,540.00 kJ/mol 5
10th Energy Level
25,290.00 kJ/mol 8
11th Energy Level
28,000.00 kJ/mol 9
12th Energy Level
31,920.00 kJ/mol 9
13th Energy Level
34,830.00 kJ/mol 9
14th Energy Level
37,840.00 kJ/mol 11
15th Energy Level
44,100.00 kJ/mol 11
16th Energy Level
47,206.00 kJ/mol 13
17th Energy Level
122,200.00 kJ/mol 1
18th Energy Level
131,000.00 kJ/mol 2
19th Energy Level
140,500.00 kJ/mol 3
20th Energy Level
152,600.00 kJ/mol 5
21st Energy Level
163,000.00 kJ/mol 5
22nd Energy Level
173,600.00 kJ/mol 4
23rd Energy Level
188,100.00 kJ/mol 4
24th Energy Level
195,200.00 kJ/mol 1
25th Energy Level
Not Available 100
26th Energy Level
Not Available 100
27th Energy Level
Not Available 0
28th Energy Level
Not Available 0
29th Energy Level
Not Available 0
30th Energy Level
Not Available 0
Electrochemical Equivalent
0.69 g/amp-hr 65
Electron Work Function
4.70 eV 10
Other Chemical Properties
Corrosion, Ionization, Solubility 0
Atomic
0
Atomic Number
26 80
Electron Configuration
[Ar] 3d6 4s2 0
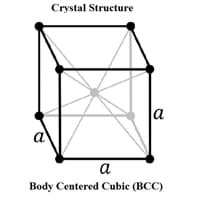
Crystal Structure
Body Centered Cubic (BCC) 0
Crystal Lattice
BCC-Crystal-Structure-.jpg#100 0
Atom
0
Number of Protons
26 79
Number of Neutrons
30 60
Number of Electrons
26 79
Radius of an Atom
0
Atomic Radius
126.00 pm 48
Covalent Radius
132.00 pm 48
Van der Waals Radius
200.00 pm 28
Atomic Weight
55.85 amu 74
Atomic Volume
7.10 cm3/mol 61
Adjacent Atomic Numbers
0
Previous Element
31 0
Next Element
30 0
Valence Electron Potential
67.00 (-eV) 20
Lattice Constant
286.65 pm 63
Lattice Angles
π/2, π/2, π/2 0
Lattice C/A Ratio
Not Available 0
Mechanical
0
Density
0
Density At Room Temperature
7.87 g/cm3 52
Density When Liquid (at m.p.)
6.98 g/cm3 35
Tensile Strength
11,000.00 MPa 1
Viscosity
Not Available 0
Vapor Pressure
0
Vapor Pressure at 1000 K
0.00 (Pa) 28
Vapor Pressure at 2000 K
36.80 (Pa) 5
Elasticity properties
0
Shear Modulus
82.00 GPa 11
Bulk Modulus
170.00 GPa 10
Young's Modulus
211.00 GPa 9
Poisson Ratio
0.29 15
Other Mechanical Properties
Ductile, Malleable, Weldable 0
Magnetic
0
Magnetic Characteristics
0
Specific Gravity
7.20 45
Magnetic Ordering
Ferromagnetic 0
Permeability
6.3 * 10-3 H/m 1
Susceptibility
2,00,000.00 1
Electrical Properties
0
Electrical Property
Conductor 0
Resistivity
96.10 nΩ·m 32
Electrical Conductivity
0.10 106/cm Ω 20
Electron Affinity
15.70 kJ/mol 34
Thermal
0
Specific Heat
0.44 J/(kg K) 13
Molar Heat Capacity
25.10 J/mol·K 43
Thermal Conductivity
80.40 W/m·K 22
Critical Temperature
Not Available 0
Thermal Expansion
11.80 µm/(m·K) 33
Enthalpy
0
Enthalpy of Vaporization
351.00 kJ/mol 23
Enthalpy of Fusion
14.90 kJ/mol 22
Enthalpy of Atomization
414.20 kJ/mol 19
Standard Molar Entropy
27.30 J/mol.K 56
|
||
|
||
|